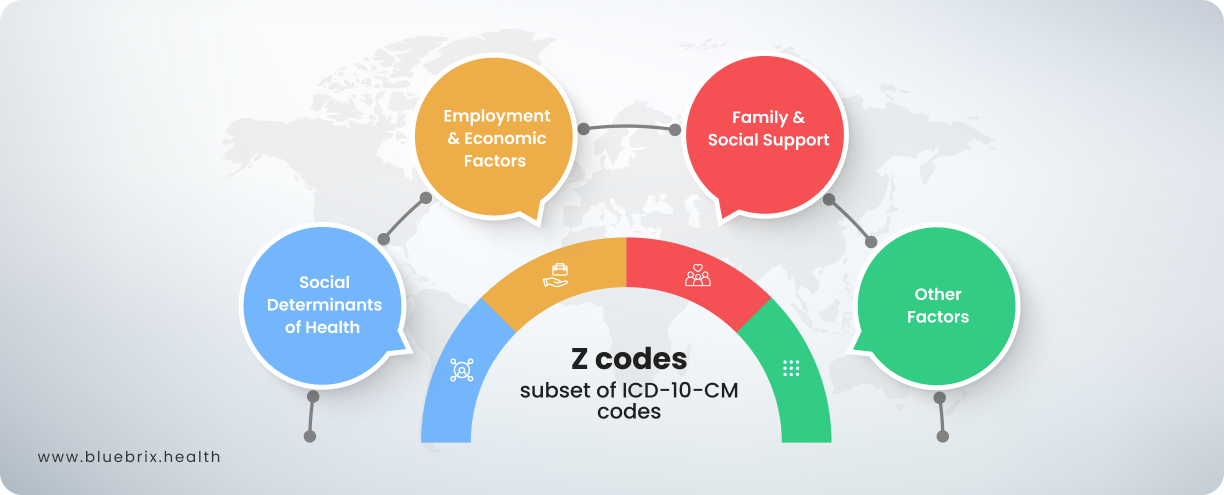
Z codes, a subset of ICD-10-CM codes, capture factors that influence health beyond traditional medical diagnoses, such as social determinants of health (SDOH), lifestyle, and environmental factors. They’re also used to record reasons for seeking healthcare that are not classified as diseases or injuries. These codes are vital for providing a more holistic understanding of patient’s conditions and needs, enabling healthcare providers to address barriers to care and improve health outcomes. In value-based care initiatives, Z codes play a critical role by identifying and documenting non-clinical factors that impact health, supporting tailored interventions, enhancing care coordination, and aligning reimbursement with patient-centered outcomes. By leveraging Z codes, healthcare organizations can drive equitable, effective care while advancing the shift toward outcomes-based models. Let us take a deeper look at it in this article.
Here are some examples of Z codes used in the ICD-10-CM system:
Social determinants of health
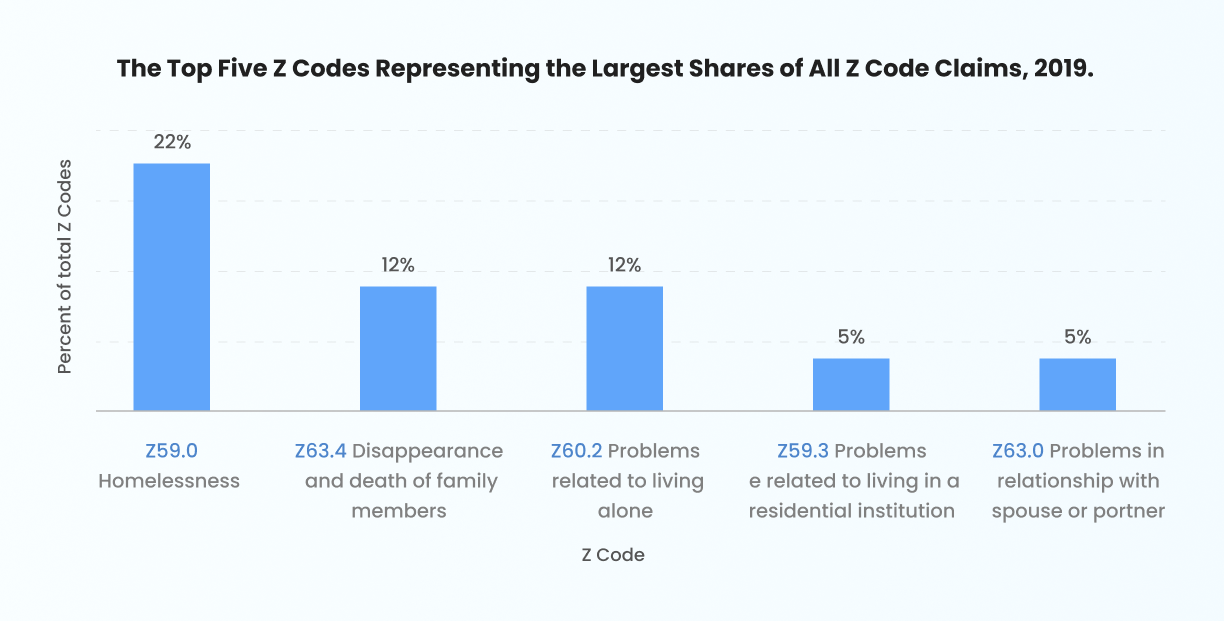
- Z59.0: Homelessness
- Z59.1: Inadequate housing
- Z59.5: Extreme poverty
- Z60.2: Problem related to living alone
- Z60.5: Target of (perceived) adverse discrimination or persecution
Employment and economic factors
- Z56.0: Unemployment
- Z56.82: Problem related to current military deployment status
- Z56.9: Other problem related to employment
Educational and occupational problems
- Z55.9: Academic or educational problem
Family and social support
- Z62.820: Parent-child relational problem
- Z63.0: Relationship distress with spouse or intimate partner
- Z63.4: Disruption of family by separation or divorce
Other factors
- Z00.4: General psychiatric examination, not elsewhere classified
- Z03.2: Observation for suspected mental and behavioral disorders
- Z09.3: Follow-up examination after psychotherapy
- Z13.4: Special screening examination for certain developmental disorders in childhood
How do Z codes provide value to both payers and providers?
Z codes offer a comprehensive understanding of patient health by connecting social and environmental factors with clinical care. This ability to document non-medical influences makes them a powerful tool for payers and providers.
For providers:
- Enhanced documentation: Z codes streamline the documentation of social determinants of health (SDOH), enabling providers to build comprehensive patient profiles that reflect social and environmental influences on health.
- Resource allocation: By identifying at-risk populations through Z codes, providers can allocate resources more strategically, focusing on interventions that address specific social and health needs.
For payers:
- Informed investments: Z codes provide payers with insights into the social factors contributing to healthcare costs, supporting data-driven decisions for funding programs that address SDOH and reduce long-term expenses.
- Collaboration opportunities: With Z code data, payers can collaborate more effectively with providers and community partners to develop population health initiatives, promote preventive care, and support proactive strategies to improve outcomes.
The role of Z codes in value-based care
Value-based care focuses on delivering high-quality, cost-effective care by addressing not just medical conditions but also the root causes of poor health outcomes. Here’s how Z codes advance this mission:
Identifying social determinants of health
Z codes enable providers to systematically capture and analyze SDOH data. This information helps identify barriers to care, such as food insecurity or lack of transportation, which can contribute to poor health outcomes and increased healthcare costs.
Risk adjustment in value-based payment models
As payers increasingly adopt risk-adjusted payment models, Z codes play a crucial role in adjusting payments based on the complexity and needs of patient populations. By capturing SDOH through Z codes, healthcare organizations can demonstrate the additional challenges faced by their patients, which may warrant higher reimbursement rates to cover the costs associated with providing care to these vulnerable groups.
Personalizing care plans
With Z codes, providers can tailor interventions to address individual patient needs such as referrals to community housing resources or case management services.
Enhancing population health management
Z codes facilitate the segmentation of populations based on social factors, allowing healthcare organizations to design targeted preventive care programs. For example, patients experiencing financial hardship may be prioritized for cost-effective care delivery models, such as telehealth or community clinics.
Supporting reimbursement models in value-based care
While Z codes are not directly tied to traditional reimbursement, they align with alternative payment models (APMs) like shared savings and bundled payments. Payers and providers can use Z code data to justify resource allocation, demonstrate the value of addressing SDOH, and secure funding for community-based programs.
Incentives for screening and reporting
Recent changes in regulations require healthcare providers to screen patients for SDOH as part of quality reporting programs, such as the Hospital Inpatient Quality Reporting program. As part of this initiative, capturing Z codes related to SDOH is not only encouraged but may also lead to additional financial incentives from Medicare when these screenings are documented during annual wellness visits.
Challenges in utilizing Z codes
Despite their potential, the adoption of Z codes faces several hurdles:
- Lack of awareness: Many providers are unfamiliar with Z codes or unsure how to incorporate them into clinical workflows.
- Incomplete documentation: Patients may not disclose SDOH factors, and providers may lack standardized tools for gathering this information.
- Limited payer incentives: Without direct reimbursement for Z codes, providers may deprioritize their use.
Overcoming barriers to Z code utilization
To fully realize the potential of Z codes in value-based care, stakeholders must address existing challenges by adopting a multifaceted approach. This involves not only understanding the importance of Z codes but also implementing practical strategies to enhance their utilization in clinical and administrative workflows.
Provider education
Clinicians are at the forefront of identifying and documenting social determinants, yet many lack the necessary training to do so effectively. By investing in provider education, healthcare organizations can ensure that clinicians understand the significance of Z codes in capturing SDOH and their impact on patient outcomes. Training programs should focus on how to document SDOH accurately and integrate this information into care planning.
Screening tools
Standardized SDOH screening tools are essential for consistent and accurate data collection. By embedding these tools into electronic health record (EHR) systems, healthcare providers can streamline the documentation process, ensuring that Z codes are captured reliably. Automated prompts and workflows within the EHR can further support clinicians in identifying and addressing SDOH needs during patient encounters.
Policy advocacy
Payers play a critical role in the adoption and impact of Z codes. Stakeholders must advocate for policies that encourage the recognition of Z codes as essential to improving health outcomes. Integrating Z codes into value-based payment models can incentivize their use, aligning financial rewards with efforts to address SDOH and reduce disparities.
Community partnerships
Effective use of Z codes extends beyond the healthcare setting. By forming partnerships with local community organizations, healthcare providers can address identified SDOH needs comprehensively. These collaborations enable a more holistic approach to care by linking patients to resources that mitigate barriers such as housing insecurity, food access, and transportation challenges.
By addressing these areas, healthcare stakeholders can unlock the full potential of Z codes, fostering a more equitable and effective value-based care ecosystem.
2025 updates in Z codes
As of 2025, there have been several important updates to Z codes that enhance their relevance in capturing social determinants of health (SDOH) and improving patient care. Notably, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has emphasized the need for healthcare providers to document SDOH using Z codes in their claims submissions, thereby promoting better understanding and management of patients’ non-medical factors affecting health. Additionally, new Z codes have been introduced to address genetic susceptibility to obesity, epilepsy and neurodevelopmental disorders, breast cancer diagnoses, sepsis aftercare, some more related to upbringing and emerging social issues, such as housing instability and food insecurity, reflecting a growing recognition of the importance of these factors in overall health outcomes. These updates aim to improve data collection and reporting, ultimately supporting value-based care initiatives by enabling more tailored and effective healthcare interventions.