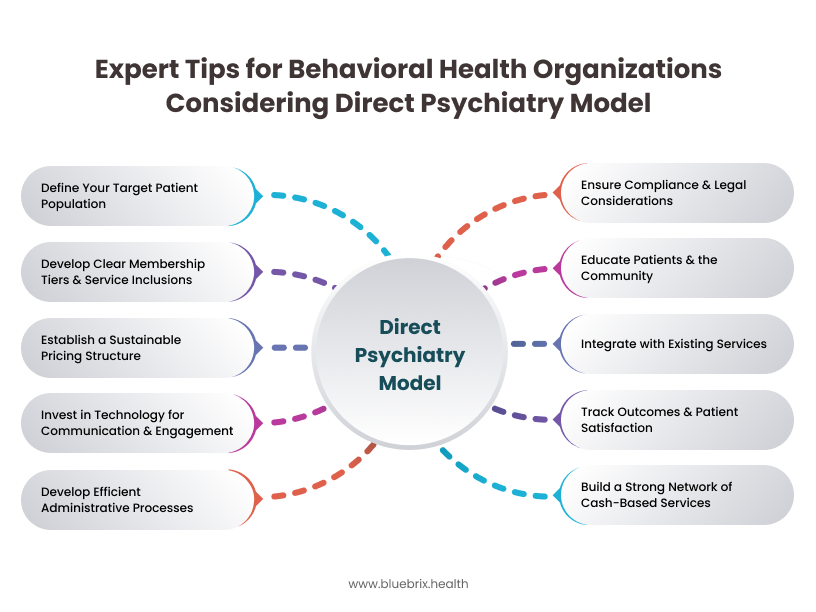
Understanding the Direct Psychiatry Model
At its core, direct psychiatry operates on a membership or subscription basis. Patients pay a recurring fee, typically monthly, directly to the psychiatric practice. This set fee covers specific services. It removes the confusion of insurance billing, copays, and deductibles for those services.
The specific services covered under a direct psychiatry membership can vary between practices, but often include:
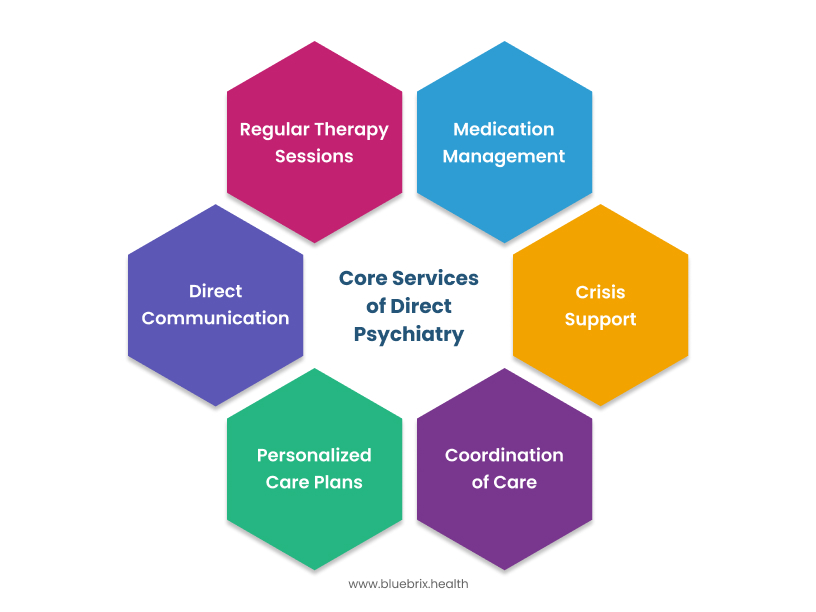
- Regular Therapy Sessions: These sessions are a key part of the model. They provide consistent and ongoing support. These sessions often have longer appointment times than usual in traditional settings.
- Medication Management: This encompasses initial evaluations, prescription management, regular follow-ups to monitor efficacy and side effects, and adjustments to medication regimens as needed.
- Direct Communication: A key difference, direct psychiatry allows easier communication between patients and their psychiatrist. This can happen through phone, email, or secure messaging. This can be invaluable for addressing urgent concerns, clarifying instructions, or providing brief check-ins between scheduled appointments.
- Crisis Support: Some psychiatry practices may provide limited help during a crisis. This can help avoid unnecessary trips to the emergency room.
- Personalized Care Plans: With more time and a direct relationship, psychiatrists can create treatment plans for each patient. These plans are tailored to meet their unique needs and goals.
- Coordination of Care: While primarily focused on psychiatric services, some direct psychiatry models may facilitate better coordination with other healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians or specialists.
Direct Psychiatry vs. Traditional Psychiatry: Key Differences
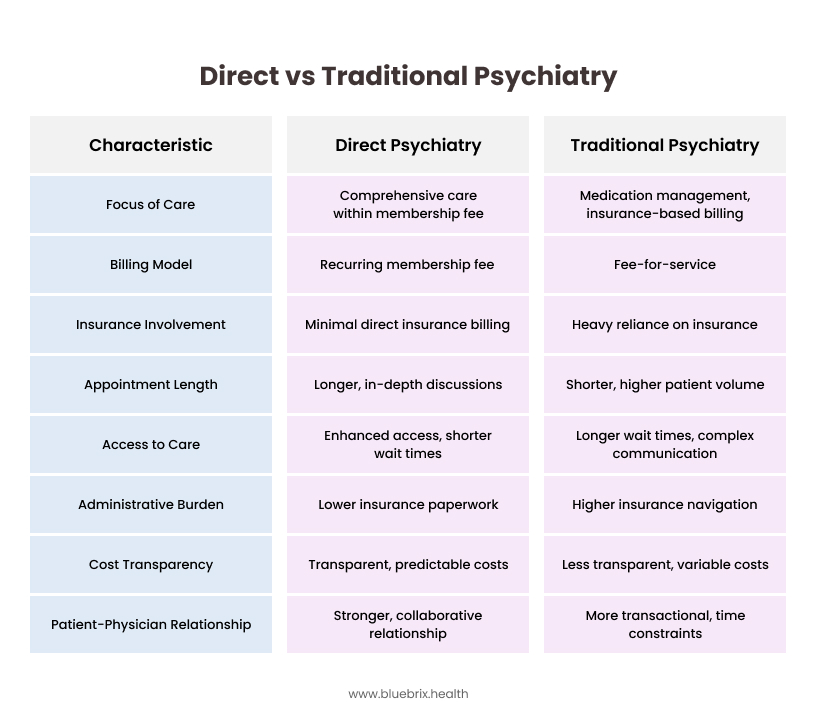
Focus Area
- Direct Psychiatry: Emphasizes a direct patient-psychiatrist relationship and comprehensive care within the scope of the membership fee.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Often focuses on shorter appointments, frequently centered around medication management, with services billed through insurance.
Billing Model
- Direct Psychiatry: Utilizes a recurring membership fee that covers a defined set of services.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Operates on a fee-for-service model, where each session or service is billed to insurance companies or directly to the patient.
Insurance Involvement
- Direct Psychiatry: Involves minimal or no direct billing to insurance companies for the services included in the membership.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Is heavily reliant on insurance authorization, billing, and reimbursement processes.
Appointment Length
- Direct Psychiatry: Appointments are typically longer, allowing for more in-depth discussions and personalized care.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Appointments are often shorter due to the need to see a higher volume of patients for reimbursement.
Access to Care
- Direct Psychiatry: Often provides enhanced access, potentially with shorter wait times for appointments and more direct communication channels.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Can involve longer wait times for appointments and more complex communication pathways due to administrative processes.
Administrative Burden (for Psychiatrist)
- Direct Psychiatry: Generally lower regarding insurance paperwork and pre-authorizations for included services.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Often higher due to the need to navigate insurance regulations, pre-authorizations, and claim denials.
Cost Transparency
- Direct Psychiatry: Offers more transparent and predictable costs for the services covered by the membership fee.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Can be less transparent, with out-of-pocket costs depending on insurance coverage, copays, and deductibles.
Patient-Physician Relationship
- Direct Psychiatry: Has the potential for a stronger, more collaborative relationship due to the direct financial link and increased time spent together.
- Traditional Psychiatry: Can sometimes be more transactional due to time constraints and the intermediary role of insurance.
Advantages of Direct Psychiatry Model
Like any healthcare model, direct psychiatry has its own set of advantages:
- Enhanced Access: Patients often experience shorter wait times for appointments and more flexible scheduling, improving access to needed care.
- Stronger Patient-Physician Relationship: The direct financial relationship and increased time per patient can foster a more trusting and collaborative therapeutic alliance.
- Personalized and Comprehensive Care: Psychiatrists have more time to conduct thorough evaluations, provide longer therapy sessions, and develop individualized treatment plans.
- Cost Transparency and Predictability: The membership fee makes it easy to see the costs for included services. This helps reduce financial surprises.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Less time spent on insurance paperwork can allow psychiatrists to focus more on patient care.
- Focus on Patient Needs: Without insurance rules, care can be tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
- Potential for Innovation: The model offers chances for new ideas. It allows for creative service delivery. This includes more frequent check-ins using technology. It also includes group therapy sessions as part of the membership.
How Direct Psychiatry Works in Practice
Challenges in Direct Psychiatry and Strategies to Overcome Them
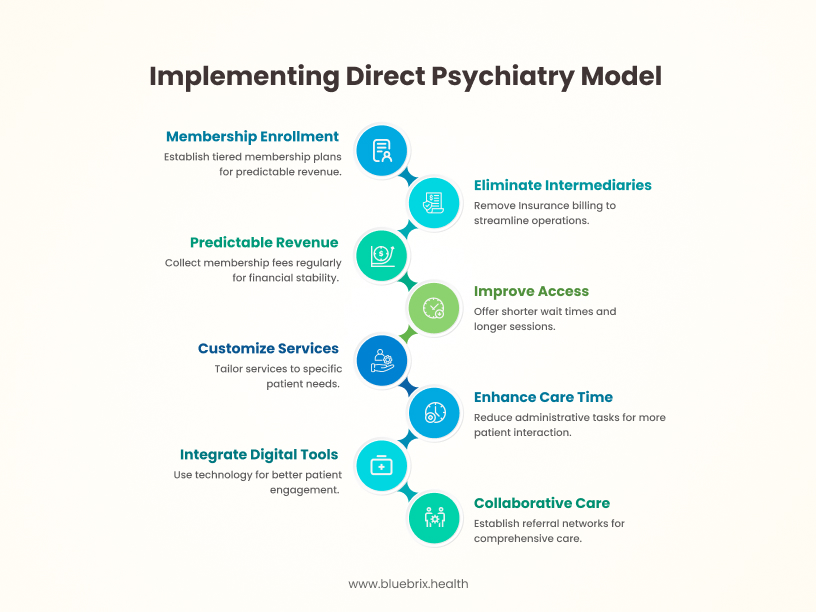
Adopting a direct psychiatry model involves a shift in both care delivery and business operations. The following outlines the typical structure and key components:
- Membership-Based Enrollment
Practices offer tiered membership plans with defined service packages and pricing. This approach enables predictable revenue streams while giving patients clarity on service expectations. - Elimination of Insurance Intermediaries
Direct psychiatry bypasses third-party payers, removing the administrative burden of insurance billing, prior authorizations, and reimbursement negotiations. This streamlines operations and allows for greater clinical autonomy. - Predictable Revenue Model
Membership fees are collected on a regular cadence—monthly, quarterly, or annually—providing financial predictability and improving cash flow stability. - Improved Access and Continuity of Care
With a limited number of patients and set membership limits, providers can give shorter wait times. They can also offer longer sessions and more regular follow-ups. This improves clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. - Customizable Service Scope
Practices can define their niche. This could be based on specific diagnoses, age groups, or treatment methods. They can then adjust their services to fit these areas. This enables alignment between clinical strengths and market demand. - More Time for High-Quality Care
Reduced administrative demands give providers more time per patient, allowing for comprehensive assessments, integrated treatment planning, and a more holistic approach to care. - Integrated Digital Support Tools
Many direct care models incorporate technology—such as secure communication platforms, symptom tracking apps, or remote monitoring tools—to support patient engagement and continuity between sessions. - Collaborative Care Infrastructure
Some practices establish formal referral networks or bundled service agreements with therapists, primary care providers, or care coordinators to ensure comprehensive care within or adjacent to the membership framework. - Transparent Pricing and Reduced Financial Friction
Clearly defined membership pricing reduces billing confusion and eliminates the need for claims processing, while also improving patient trust and satisfaction with the financial aspects of care.
Challenges in Direct Psychiatry and Strategies to Overcome Them
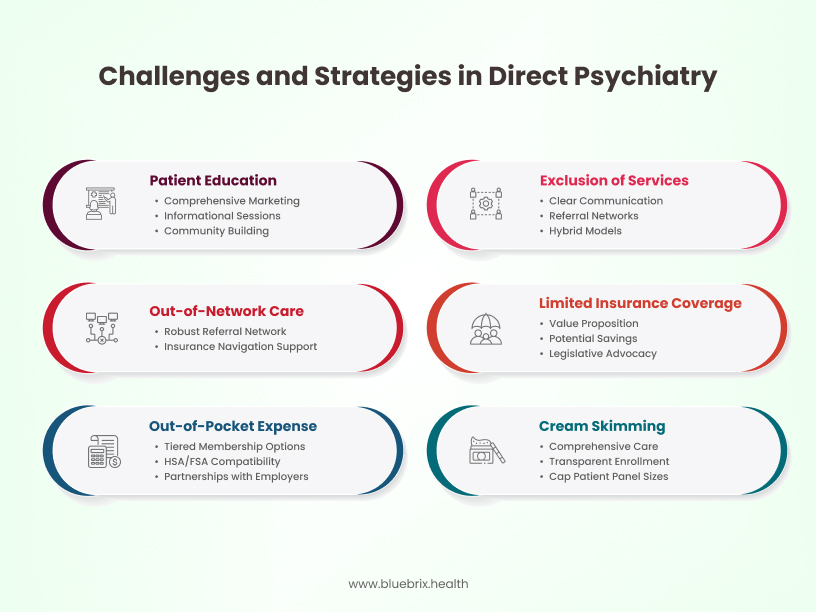
Challenge 1: Out-of-Pocket Expense for Membership
The recurring membership fee is an extra cost for patients. This can be a big barrier for individuals and families. This is especially true for those with lower incomes or those already facing other healthcare costs.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Tiered Membership Options: Provide different membership levels. Each level has unique services and prices. This helps meet various budgets and needs. A basic tier could focus on core services. This might include regular check-ins and medication management. More comprehensive tiers could offer extra therapy time or resources.
- Health Savings Account (HSA) and Flexible Spending Account (FSA) Compatibility Information: Clearly educate potential members on whether their membership fees are eligible for HSA or FSA reimbursement, which can help offset the cost.
- Partnerships with Employers: Collaborate with local businesses to offer direct psychiatry memberships as part of their employee benefits packages, similar to the DPC model highlighted in the podcast. This can make the model more accessible to a larger population.
- Sliding Scale or Financial Assistance Programs: For individuals facing financial hardship, consider implementing a sliding scale fee structure or offering limited financial assistance programs based on income and need.
- Demonstrate Long-Term Value: Clearly articulate how the direct psychiatry model can potentially lead to lower overall healthcare costs by preventing crises, reducing the need for emergency room visits, and promoting better long-term mental health management.
Challenge 2: Exclusion of Certain Necessary Services
The membership fee may not pay for all the mental health services a patient needs. This includes intensive outpatient programs (IOPs), inpatient hospitalization, specialized testing like neuropsychological evaluations, or long-term residential treatment. This can lead to additional costs and the need to navigate insurance for these external services.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Clear Communication of Inclusions and Exclusions: Be transparent about what services are covered under the membership and what will incur additional fees or require external referrals.
- Establish Referral Networks: Develop strong relationships with trusted providers and facilities offering these specialized services, ideally those with transparent cash-based pricing or who are in-network with common insurance plans in the area.
- Facilitate Insurance Navigation: While the core services bypass insurance, offer support to members in understanding their insurance benefits and navigating the process for accessing services outside the membership.
- Consider Hybrid Models: Explore the possibility of a hybrid model that combines a core direct psychiatry membership with the option to bill insurance for certain higher-cost or less frequently needed services. This requires careful legal and ethical consideration.
- Advocate for Transparent Pricing: Encourage partner providers to offer transparent cash prices for services that might be needed by direct psychiatry members, mirroring the DPC experience with labs and imaging.
Challenge 3: Limited Insurance Coverage for Membership Fees
Traditional health insurance plans typically do not cover direct pay membership fees, meaning patients bear the full cost out-of-pocket. This can be a deterrent for individuals who rely heavily on their insurance benefits.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Focus on Value Proposition: Emphasize the value and benefits of direct psychiatry that may not be fully realized through traditional insurance-based care, such as increased access, longer appointments, and a stronger therapeutic relationship.
- Educate on Potential Savings: Highlight potential long-term cost savings through proactive care and reduced reliance on more expensive interventions like emergency room visits.
- Promote HSA/FSA Eligibility: As mentioned earlier, clearly communicate if membership fees qualify for HSA/FSA use.
- Legislative Advocacy: Engage in advocacy efforts to educate policymakers and insurance providers about the benefits of direct pay models and explore the possibility of future insurance coverage or integration.
- Offer Payment Plans: Consider offering flexible payment plans for membership fees to make them more manageable for patients.
Challenge 4: Potential for “Cream Skimming” (Selecting Healthier Patients)
There’s a concern that direct psychiatry practices might be incentivized to attract and retain healthier patients who require fewer services, potentially leaving individuals with more complex or chronic conditions in the traditional system.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Focus on Comprehensive Care for All Members: Design the model to provide high-quality, comprehensive care regardless of the complexity of a patient’s condition within the defined scope of services.
- Transparent Enrollment Policies: Establish clear and non-discriminatory enrollment policies that do not exclude individuals based on their mental health history or the complexity of their needs.
- Demonstrate Success with Diverse Patient Populations: Showcase positive outcomes and high satisfaction rates among patients with a range of mental health conditions.
- Cap Patient Panel Sizes: Maintain manageable patient panel sizes to ensure that psychiatrists have adequate time to provide quality care to all members, including those with more complex needs.
- Collaborate with Specialists: Develop strong referral networks for patients whose needs exceed the scope of the direct psychiatry practice, ensuring a seamless transition to appropriate specialized care.
Challenge 5: Navigating Out-of-Network Care and Referrals
When patients require services outside the direct psychiatry practice (e.g., hospitalization, specialized therapy), they may face out-of-network costs and the complexities of dealing with their insurance for these referrals.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Develop a Robust Referral Network: Establish relationships with in-network specialists and facilities whenever possible to minimize out-of-pocket costs for members.
- Provide Support with Insurance Navigation for Referrals: Offer administrative assistance to members in understanding their insurance benefits and navigating the referral process for out-of-network care.
- Advocate for Transparent Pricing with Referral Partners: Encourage referred providers to offer transparent cash prices for members who may have high deductibles or limited out-of-network coverage.
- Consider Collaborative Care Agreements: Explore formal agreements with other providers to streamline referrals and communication.
Challenge 6: Patient Education and Understanding of the Model
The direct psychiatry model is still relatively new, and potential patients may not fully understand how it works, its benefits, and its limitations compared to traditional insurance-based care.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Comprehensive Marketing and Educational Materials: Develop clear and informative website content, brochures, and presentations explaining the direct psychiatry model, its benefits, service inclusions, and costs.
- Develop Targeted Marketing and Outreach: Design marketing plans that show the unique benefits of direct psychiatry. These benefits include better access, personalized care, clear costs for services, and a direct relationship between patients and psychiatrists. Tailor these messages to resonate with the identified target patient population.
- Host Informational Sessions and Webinars: Conduct online and in-person sessions to answer questions and address concerns from potential members.
- Share Testimonials and Success Stories: Highlight positive experiences from current members to illustrate the value of the model.
- Clearly Differentiate from Traditional Psychiatry: Emphasize the key differences and advantages of direct psychiatry, such as increased access and personalized care.
- Foster a Sense of Community: Explore opportunities to build a supportive community around the practice. This could include optional virtual or in-person support groups. It may also offer educational workshops for members. Online forums can be created while keeping privacy. These options will enhance the membership’s value and encourage peer support.
- Implement Robust Data Collection and Outcome Measurement: Establish systems for collecting data on patient outcomes, satisfaction levels, and retention rates. This data is crucial for demonstrating the effectiveness of the direct psychiatry model, identifying areas for improvement, and informing marketing efforts.
By addressing these potential downsides and using smart strategies, behavioral health organizations can create successful direct psychiatry practices. These practices can provide great benefits to both patients and providers.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape of Direct Psychiatry
The innovative direct psychiatry model, while offering numerous benefits, operates within a complex web of healthcare regulations. It is very important for both practitioners and patients to understand and follow these rules. The rules can change a lot based on the state or area. This makes careful research and legal advice very important.
State-Specific Regulations: A Patchwork of Rules
Healthcare in the United States is largely governed at the state level. This means that the legal requirements for practicing psychiatry, offering telemedicine services, and operating direct pay healthcare models can differ considerably from one state to another. Behavioral health organizations considering direct psychiatry must meticulously research and comply with the specific regulations of each state where they intend to provide services. This includes understanding licensing requirements for psychiatrists, rules surrounding the patient-physician relationship, and any specific laws pertaining to direct healthcare agreements.
Licensing Requirements: Ensuring Qualified Practitioners
Regardless of the payment model, psychiatrists practicing in a direct psychiatry setting must hold a valid and active medical license in the state where the patient is located during the time of service. This fundamental requirement ensures that patients are receiving care from qualified and credentialed professionals. For practices offering telehealth services across state lines, understanding and adhering to interstate licensing regulations is crucial and can sometimes involve obtaining licenses in multiple states.
Telehealth Regulations: Bridging Geographical Barriers
Direct psychiatry often leverages telehealth technologies to enhance accessibility and convenience. However, the use of video conferencing, phone consultations, and secure messaging platforms is subject to specific state telehealth regulations. These rules can address aspects such as the establishment of the patient-physician relationship via telehealth, requirements for informed consent, the types of mental health services that can be delivered remotely, and data security protocols. Compliance with these evolving regulations is vital for any direct psychiatry practice utilizing virtual care.
HIPAA Compliance: Protecting Patient Privacy
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) remains a cornerstone of healthcare regulation in the United States. Direct psychiatry practices, despite their alternative payment model, are still obligated to comply fully with HIPAA regulations to protect the privacy and security of patient health information. This includes implementing administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure1 of protected health information.

Prescribing Regulations: A Critical Aspect of Psychiatric Care
For direct psychiatry practices that include medication management, adherence to state and federal prescribing regulations is non-negotiable. This includes understanding rules related to electronic prescribing, controlled substances, and the establishment of a valid patient-physician relationship before prescribing. Telehealth prescribing, in particular, may have specific requirements that need to be carefully followed.
Contractual Agreements: Defining the Patient-Practice Relationship
A clear and legally sound membership agreement is essential for direct psychiatry practices. This contract should explicitly outline the services included in the membership fee, any services that incur additional costs, the payment terms, termination policies for both the patient and the practice, policies regarding communication and response times, and patient rights and responsibilities. Consulting with legal counsel to draft a comprehensive and compliant membership agreement is highly recommended.
Ethical Considerations: Beyond Legal Requirements
While adhering to legal regulations is crucial, direct psychiatry practices must also navigate ethical considerations. This includes making sure everyone can access care within the membership model. It also involves managing any conflicts of interest from the direct financial relationship.
Additionally, it is important to keep professional boundaries in more frequent and direct communication with patients. Transparency and clear communication are key to upholding ethical standards.
“Insurance” vs. “Membership”: A Crucial Distinction
It is vital to clearly communicate to potential patients that a direct psychiatry membership is not a substitute for comprehensive health insurance. The membership fee covers a defined set of services within the direct practice. Patients will still likely need health insurance to cover services outside this scope, such as hospitalizations, emergency care, specialized testing not offered in-house, and care from other specialists. Misrepresenting the membership as a form of insurance can lead to legal and ethical issues.
The Necessity of Legal Consultation
Healthcare rules can be complicated and differ by state. Therefore, it is important for any behavioral health organization to seek advice from experienced legal counsel. This is especially true before starting a direct psychiatry model.
A lawyer who specializes in this area can help you understand state laws. They can draft membership agreements that follow the rules. They also ensure compliance with HIPAA. Additionally, they can address other legal and regulatory issues that relate to your practice and location.
Payment Processing and Financial Regulations
Direct psychiatry practices must also adhere to regulations concerning payment processing for membership fees and any non-included services. This includes ensuring secure handling of financial data, complying with relevant data security standards (like PCI DSS if accepting credit card payments), and potentially understanding state laws related to subscription-based services or recurring billing.
Liability and Malpractice Considerations
It’s crucial to remember that the direct pay model does not alter a psychiatrist’s professional liability. Maintaining adequate malpractice insurance coverage remains essential for protecting both the practitioner and the practice. The direct relationship emphasizes the importance of clear communication and documentation to mitigate potential risks.
By proactively addressing the regulatory landscape, direct psychiatry practices can operate ethically, legally, and sustainably, ultimately providing high-quality mental healthcare within a clear and compliant framework.
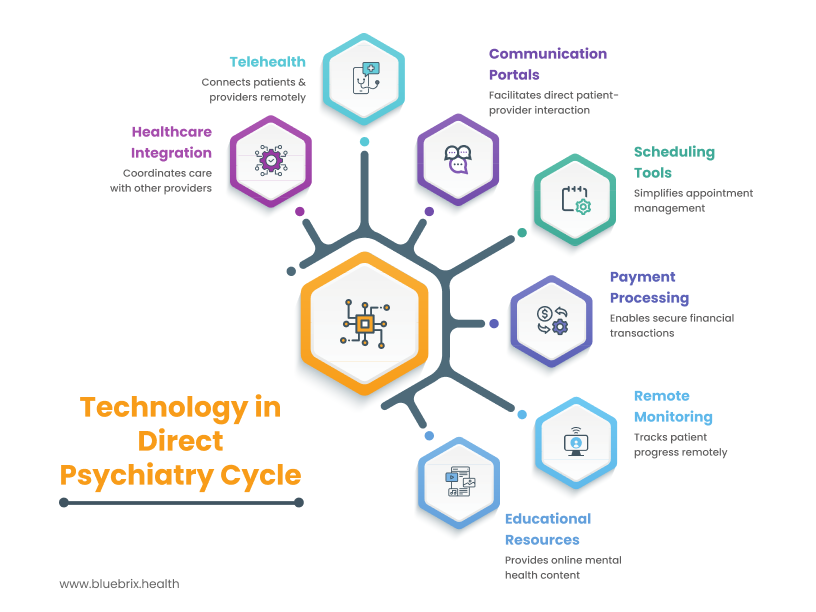
How Technology Enhances Direct Psychiatry
Technology plays a pivotal role in enabling and optimizing the direct psychiatry model, enhancing both the patient and provider experience. From facilitating seamless communication to streamlining administrative tasks, the strategic use of digital tools can significantly contribute to the success and scalability of direct psychiatry practices.
- Telehealth for Expanded Reach and Convenience: As previously discussed, telehealth platforms are crucial for direct psychiatry, allowing practitioners to connect with patients across geographical distances, offering greater convenience and accessibility, particularly for those in rural areas or with mobility challenges.
- Direct Communication Portals: Secure messaging platforms and patient portals facilitate direct and efficient communication between patients and their psychiatrists for non-urgent queries, appointment scheduling, and sharing of relevant information. This direct line of communication strengthens the patient-provider relationship and can improve patient engagement.
- Streamlined Scheduling and Appointment Management: Online scheduling tools and integrated calendar systems simplify appointment booking and management for both patients and staff, reducing administrative overhead and improving convenience.
- Secure Payment Processing: Technology enables seamless and secure processing of membership fees and payments for any additional services, contributing to efficient financial management.
- Remote Monitoring and Progress Tracking: Certain technologies, such as mood tracking apps or wearable device integration (where appropriate and with patient consent), can aid in remote monitoring of patient progress and provide valuable insights for treatment adjustments.
- Educational Resources and Digital Content Delivery: Online platforms can be used to share educational materials, self-help resources, and personalized content with members, enhancing their understanding and engagement with their mental health care.
- Integration with Other Healthcare Providers (where applicable): Secure digital platforms can facilitate the sharing of relevant information with other healthcare providers (with patient consent), promoting better coordination of care.
The Limitations of Cookie-Cutter EHRs for Direct Psychiatry
While Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are essential for any modern medical practice, a generic, “cookie-cutter” EHR designed primarily for traditional insurance-based models often falls short of meeting the unique needs of direct psychiatry practices:
- Focus on Billing and Coding: Standard EHRs are heavily oriented towards generating billing codes (CPT, ICD-10) required for insurance claims. In a direct pay model, these features are largely unnecessary and can clutter the interface, making it less efficient for the core tasks of patient care and communication.
- Complex Authorization Workflows: Traditional EHRs often incorporate intricate workflows for pre-authorizations and referrals mandated by insurance companies. These features are irrelevant in a direct pay setting and can add unnecessary complexity.
- Limited Membership Management Features: Generic EHRs typically lack features specifically designed for managing memberships, such as recurring billing, different membership tiers, tracking membership status, and communication tools tailored to members.
- Inefficient Direct Communication Tools: While some EHRs offer basic messaging, they may not be as user-friendly or integrated as purpose-built communication platforms that facilitate seamless dialogue between patients and providers outside of scheduled appointments.
- Lack of Cash-Based Service Pricing and Tracking: Standard EHRs are designed for insurance-based pricing structures and may not efficiently handle or track cash-based payments for services not included in the membership.
- Reporting and Analytics Inefficiencies: Reports generated by standard EHRs are often geared towards billing and insurance-related metrics, which are not the primary KPIs for a direct psychiatry practice focused on patient engagement, outcomes, and membership retention.
How a Purpose-Built Behavioral Health EHR Can Help Direct Psychiatry Flourish
A behavioral health EHR specifically designed with the direct psychiatry model in mind can offer significant advantages:
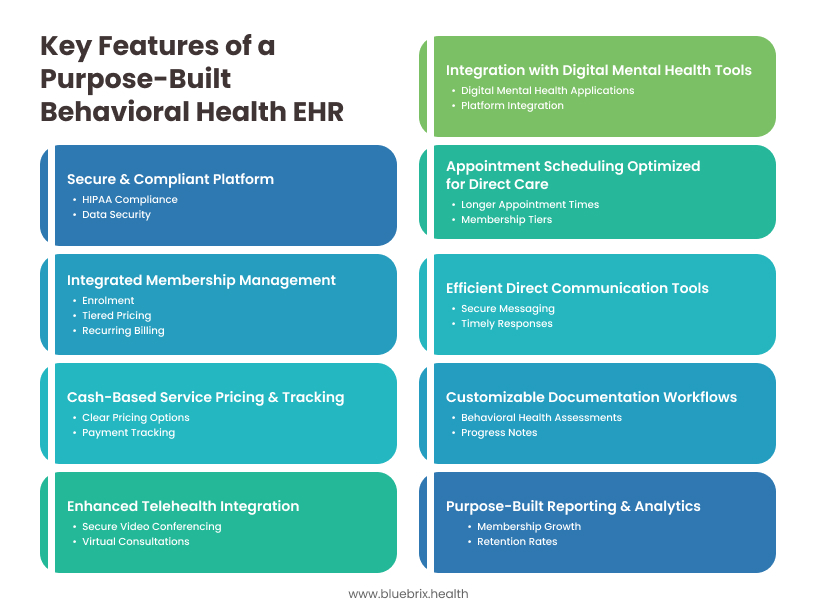
- Integrated Membership Management: Features tailored for managing memberships, including enrollment, tiered pricing, recurring billing, membership status tracking, and automated reminders.
- Efficient Direct Communication Tools: Secure and user-friendly messaging platforms designed for easy communication between patients and providers, facilitating timely responses and check-ins.
- Customizable Documentation Workflows: EHR templates and workflows specifically designed for behavioral health assessments, progress notes, and treatment plans, without the unnecessary fields related to insurance billing.
- Cash-Based Service Pricing and Tracking: Streamlined tools for managing and tracking payments for services outside the membership, with clear and transparent pricing options.
- Enhanced Telehealth Integration: Seamless integration with secure video conferencing platforms for virtual consultations, often within the EHR interface.
- Purpose-Built Reporting and Analytics: Dashboards and reports focused on key metrics for direct psychiatry, such as membership growth, retention rates, patient engagement, and outcome measures relevant to mental health.
- Secure and Compliant Platform: Built with HIPAA compliance and data security as core principles, ensuring the protection of sensitive patient information.
- Appointment Scheduling Optimized for Direct Care: Flexible scheduling tools that accommodate longer appointment times and different membership tiers.
- Integration with Digital Mental Health Tools: Potential for seamless integration with other relevant digital mental health applications and platforms.
By leveraging a purpose-built behavioral health EHR, direct psychiatry practices can operate more efficiently, enhance patient engagement, streamline administrative tasks, and ultimately focus on delivering high-quality, personalized mental healthcare within the subscription-based model. This tailored technological infrastructure can be a significant driver for the flourishing of direct psychiatry.