
Healthcare environments handle a vast amount of sensitive information, from personal health records to critical medical data, making robust access control essential for protecting patient privacy and ensuring operational security. In healthcare, access control is essential for data protection and operational security, ensuring only authorized personnel access sensitive areas and resources. Effective access control ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific areas, data, and resources, minimizing risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
Why Access Control is Essential in Healthcare
Healthcare providers leverage access control to secure digital systems by restricting access to electronic medical records (EMRs) to authorized individuals only. This safeguard protected health information (PHI) from breaches and unauthorized disclosures. Similarly, physical access control restricts entry to critical areas such as medication dispensaries and labs, minimizing risks such as theft and misuse of hazardous substances.
Beyond operational benefits, access control systems are integral to achieving compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and Meaningful Use certifications. These regulations require organizations to maintain stringent data security and privacy standards. Role-based access control aligns with compliance mandates by granting users access only to the information necessary for their specific roles, reducing opportunities for unauthorized data usage or accidental breaches.
Audit trails further enhance compliance efforts by maintaining detailed logs of who accessed what information and when. This capability not only supports internal monitoring but also provides crucial evidence for regulatory audits and investigations, demonstrating proactive risk management. By integrating access controls with comprehensive audit mechanisms, healthcare organizations can foster trust, streamline operations, and maintain adherence to critical legal standards.
Access Control and Compliance in Healthcare
With the increasing digitization of healthcare data, adherence to access control policies has become essential for healthcare providers, not only to protect patient privacy but also to comply with stringent regulations like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in the European Union.
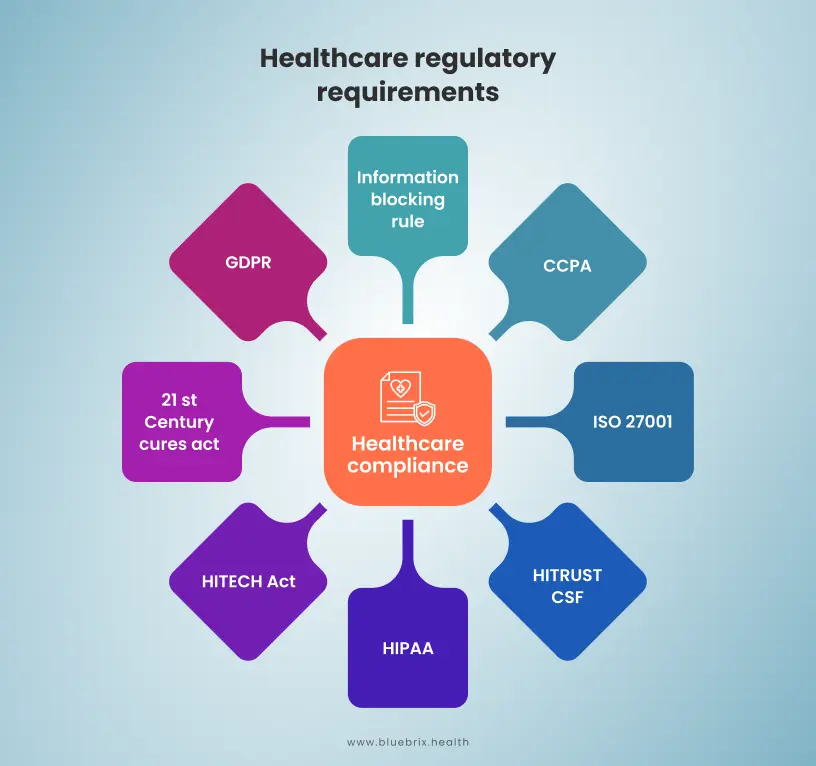
Healthcare Regulatory Requirements
Healthcare organizations face multiple compliance requirements to ensure data protection and privacy. Healthcare regulatory compliance is heavily influenced by robust access control systems that protect sensitive patient data and ensure only authorized personnel can access it. Under HIPAA and the HITECH Act, healthcare organizations must limit access to electronic protected health information (ePHI) to safeguard patient privacy and ensure data integrity. The 21st Century Cures Act and the Information Blocking Rule emphasize secure access to patient data while preventing practices that restrict data sharing, highlighting the need for flexible but controlled access systems. Additionally, the GDPR in the EU and the CCPA in California mandate strict access protocols to protect individuals’ personal data, requiring healthcare entities to implement access controls that prevent unauthorized use or breaches. ISO 27001 and HITRUST CSF provide frameworks for healthcare organizations to establish access control measures as part of broader security management, further reinforcing compliance efforts. These regulations collectively underscore access control as critical for compliance, ensuring that healthcare providers protect patient data, comply with privacy laws, and support secure, interoperable data exchange.
Enhancing Compliance with Access Control
Access control helps safeguard sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA and GDPR. Access control systems limit access to confidential areas and data to only authorized personnel, significantly reducing risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, and operational inefficiencies. By integrating audit trails and real-time monitoring, these systems enable healthcare providers to document and prove compliance while facilitating quick responses to potential security issues. Additionally, access control can secure medicine dispensaries, sensitive patient areas, and administrative systems, reducing human error and maintaining a secure environment for patients and staff. By improving visibility and ensuring access is traceable and restricted, healthcare facilities enhance overall compliance, increase patient trust, and support a culture of safety and accountability.
Types of Access Control Systems in Healthcare
In healthcare settings, securing access to sensitive data, patient areas, and digital systems is essential for maintaining privacy, safety, and regulatory compliance. Access control systems serve as critical components in managing who can enter physical spaces or access digital records. With various types of access controls, healthcare facilities can tailor security measures to their unique needs. The primary types include physical access control, digital access control, and identity and access management (IAM) solutions, each contributing to an integrated approach for protecting healthcare environments.
Physical Access Control

Physical access control limits entry to restricted areas within healthcare facilities, such as operating rooms, data centers, and pharmacies, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access these sensitive locations. Physical control methods include:
Badge Systems and Key Cards: Common in hospitals, these allow personnel with proper authorization to enter specific areas by scanning their badge at entry points.
Biometric Scanners: Technologies like fingerprint and iris scanners are used for high-security areas, adding an extra layer of security and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Geofencing: This technology can restrict physical movement or limit access to Electronic Health Records based on specific geolocations or IP addresses. By defining virtual boundaries, geofencing ensures that only authorized users within approved locations—such as hospital premises or designated workstations—can access sensitive patient data. It also provides an additional layer of security by preventing unauthorized access from outside the permitted geographic zones, safeguarding confidential information and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Digital Access Control
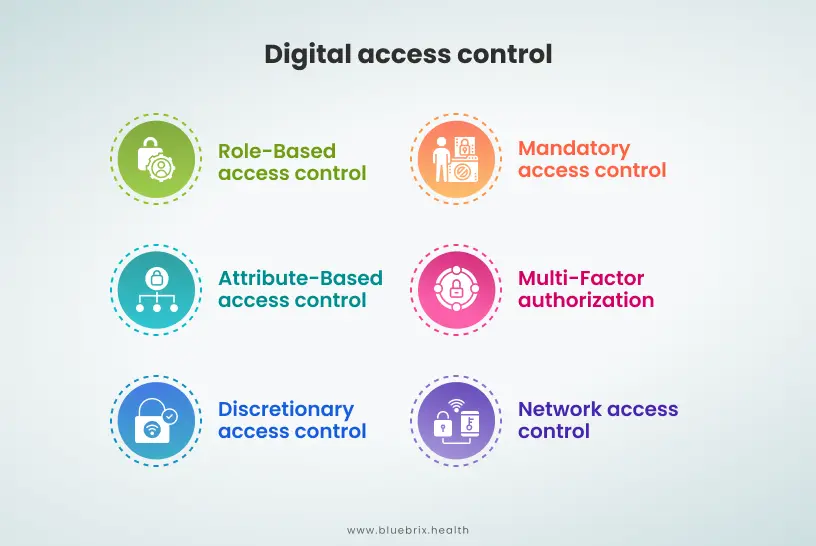
Digital access control focuses on securing electronic systems, including patient records, medical billing information, and diagnostic tools, to ensure that only authorized users can access these systems.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grants access based on job roles, ensuring that healthcare personnel access only the data necessary for their specific duties, such as doctors viewing patient files but not financial records.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): ABAC offers a more dynamic approach by allowing access based on a combination of attributes, such as user role, location, and time. This ensures that healthcare staff access systems only when certain conditions are met, like restricting access to certain data from off-site locations, during specific times, user-roles etc.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC): In this model, the data owner controls access permissions, allowing flexibility but requiring vigilant monitoring to prevent unauthorized access by users with excessive privileges.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC): This strict model enforces access based on policies set by the organization rather than individual discretion, making it ideal for sensitive healthcare data where consistent, high-level security is required.
Multi-Factor Authorization (MFA): MFA adds a layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, texted codes or biometric verification, to confirm a user’s identity before granting access.
Network Access Control (NAC): NAC manages which devices can connect to hospital networks, preventing unregistered or unsecured devices from accessing sensitive systems.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solutions
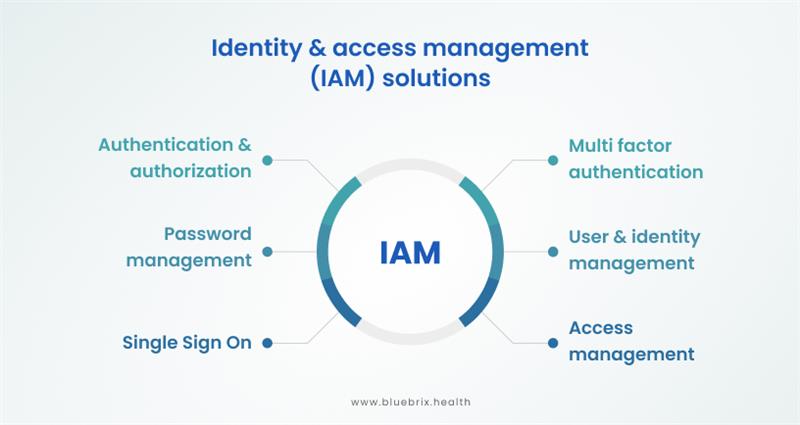
IAM solutions provide a unified approach to managing digital identities across healthcare systems, helping maintain security across diverse platforms and applications.
Single Sign-On (SSO): This solution allows users to access multiple applications with a single login, reducing the need for multiple passwords and improving workflow efficiency while keeping track of user activities.
Automated Provisioning and De-provisioning: IAM systems can automate account setup for new employees and terminate access immediately when personnel leave, minimizing security risks.
Audit Trails and Reporting: IAM solutions log access records, enabling healthcare administrators to monitor and review access points for compliance, detect anomalies, and generate regulatory reports when required.
By implementing these layers of access control, healthcare organizations enhance the security of both physical and digital assets, reduce unauthorized access risks, and support compliance with healthcare standards.
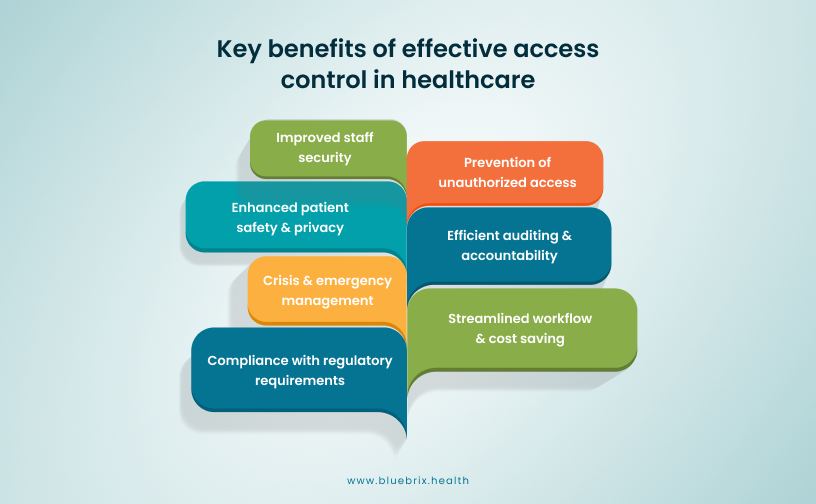
Key Benefits of Effective Access Control in Healthcare
Challenges of Implementing Access Control in Healthcare Settings
Identity and Access Management
Managing Identities and Personas: Handling numerous identities across providers, staff, and third parties.
Licensing and Credentialing for IT Access: Ensuring only licensed, credentialed, and trained professionals access IT resources.
Trusted Identities: Verifying that only trusted identities are granted access to maintain security.
Access Control Models: Selecting the best-fit access model (role-based, attribute-based) for diverse healthcare roles.
Data Privacy and Security Compliance
Protecting Sensitive Data (PHI): Ensuring PHI protection under strict regulations to prevent breaches.
Privacy: Meeting HIPAA and similar privacy standards to ensure authorized-only access to patient data.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to legal standards (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) with thorough documentation for audits.
Cybersecurity and Network Security
Cybersecurity: Addressing the advanced, targeted cyber threats specific to healthcare.
Network Security Issues: Securing network access to prevent vulnerabilities in distributed networks.
Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing systems for tracking access activity and detecting unauthorized behavior.
Operational Efficiency and User Access Needs
Ensuring Quick and Efficient Access for Providers: Balancing access speed and security to avoid delays in patient care.
Distributed IT Systems: Managing access control across multiple locations within healthcare’s complex IT environments.
Legacy Systems: Integrating modern access solutions with outdated healthcare systems to enhance security.
Access Control Policy and Permissions Management
Policy Management: Developing and enforcing clear policies amidst healthcare’s dynamic environment.
Excessive Permissions and Exceptions: Controlling “privilege creep” to ensure users don’t accumulate unnecessary permissions.
Technology and Implementation Challenges
Access Control Models: Choosing an appropriate access control model to meet the varied needs of healthcare roles.
System Interoperability: Access control systems must often integrate with existing healthcare IT systems. Interoperability issues between different platforms can hinder seamless access and complicate data sharing, resulting in delays and potential security risks.
Standardization and Usability: Lack of standardization across healthcare facilities complicates implementation. Additionally, user-friendly interfaces are essential for healthcare professionals to access data efficiently without extensive training, but creating such interfaces poses a design challenge.
Cost Constraints: Implementing robust access control systems, especially those incorporating advanced cybersecurity features, can be costly. Budget constraints in many healthcare facilities make it difficult to adopt or upgrade these technologies.
Scalability and Complexity of Implementation: Healthcare environments are complex, and access control solutions need to be scalable to adapt to growing patient data and varying levels of access. Implementing scalable solutions without disrupting day-to-day operations is a challenge.
Best Practices for Access Control in Healthcare
To ensure patient safety, data security, and operational efficiency, healthcare facilities implement access control best practices as follows:
RBAC & ABAC: Ensures that each staff member has only the necessary access for their responsibilities, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Multi-Factor Authentication: Strengthens security by requiring multiple forms of verification before access is granted.
Regular Audits: Helps identify discrepancies, remove outdated permissions, and maintain updated access policies, ensuring security standards are upheld.
Policy Development and Training: Empower staff to follow security protocols correctly and minimize accidental breaches.
Utilizing Electronic and Biometric Systems: Supports robust, real-time monitoring and management of access permissions.
These practices not only safeguard patient data but also support healthcare compliance and accountability.
blueBriX Access Control for Secure and Customized Information Access
The blueBriX platform provides a sophisticated access control system to ensure that both patients and healthcare providers can securely and effectively manage access to sensitive health information. With various access control features, blueBriX enhances data privacy and compliance with healthcare standards, allowing controlled access based on roles, attributes, and individual permissions. With blueBriX access control as an extended solution within a newly built customer application, organizations can effectively mitigate the outlined challenges. This robust solution ensures enhanced security, streamlined operations, and compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, blueBriX accelerates the application’s speed to market while significantly reducing development and operational costs, enabling a faster and more efficient market launch.
Program Management Access Control
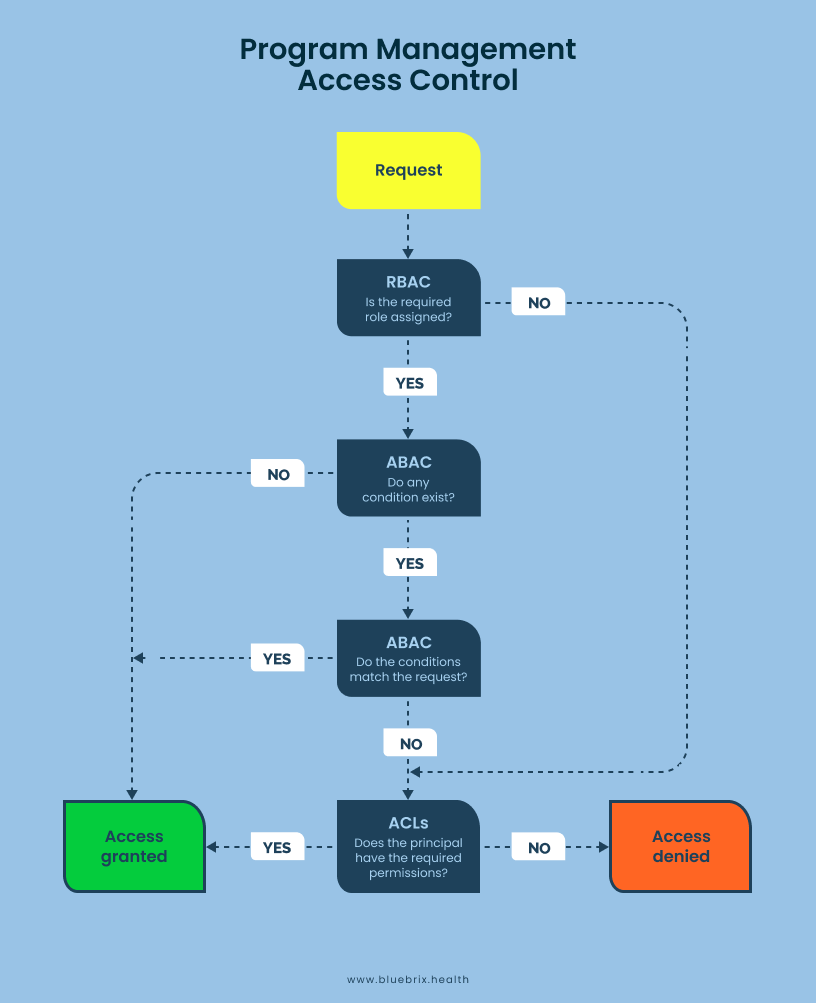
blueBriX allows organizations to manage permissions at a granular level through Program Management Access Control, which includes:
Access Control List (ACL): blueBriX’s ACL feature lets administrators assign permissions for different user groups. By using toggle buttons, administrators can define specific permissions for each module and setting, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive areas within the platform. This flexibility enhances security by allowing precise control over who sees and modifies critical data.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): With RBAC, blueBriX lets you assign permissions based on user roles within the healthcare organization, ensuring that each user has access only to information relevant to their job. This setup prevents unauthorized data access and aligns with compliance requirements for safeguarding patient information effectively.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): ABAC in blueBriX uses user attributes (such as department, clearance level, or location) to determine access rights dynamically. This flexible control helps accommodate complex organizational structures and enables access based on real-time data attributes, such as time or user location, offering tailored and secure access control.
Asset-Based Access: This feature restricts access based on the specific asset or resource being accessed. In blueBriX, it enables secure handling of patient data and resources, ensuring that only those with a legitimate need have access to a particular patient’s information, fostering a high level of privacy and data security.
Break-the-Glass Privacy: For emergency situations, blueBriX’s “Break-the-Glass” feature allows temporary access to critical patient health information. This feature grants emergency access to authorized providers under specific conditions, ensuring patient safety while maintaining data security.
Patient-Controlled Access: Patients have full control over their health records in blueBriX. Additionally, they can authorize caregivers or family members to access certain parts or the entirety of their Personal Health Information (PHI), enabling personalized and transparent data sharing in line with privacy preferences.
Forms Administration Access Control
In blueBriX, administrators can define access levels for different form types, such as HTML-based or layout-based forms, using three primary permissions:
Save Control: Allows designated users to edit and save form data, supporting data entry and updates by authorized personnel.
View Control: Restricts users to view-only access, ensuring sensitive forms can be reviewed but not altered.
Denied: Prohibits any access to the form for certain users, preventing exposure of sensitive information.
Permissions can be tailored for individual users or user groups, and a color-coded system provides a clear visual representation of different access levels. This streamlined approach promotes efficient information access management, ensuring compliance while simplifying the user experience.
Document Access Control
blueBriX implements a robust document access control system to ensure patient records are securely managed within its digital health platform. Patient records stored in designated folders are protected by stringent access controls that limit document access to specific authorized users. This controlled access approach safeguards patient health documents, allowing only designated healthcare professionals to view or modify sensitive data based on their roles and permissions within the platform.
blueBriX’s access control features allow administrators to set access levels according to predefined roles and user-specific permissions. This includes implementing “view-only” permissions for individuals who need to review information without making changes and “full access” permissions for those authorized to update records. Through this setup, blueBriX ensures both security and compliance with data protection regulations, enhancing the privacy of patient information while supporting accurate, timely data access for care providers.
Through these comprehensive access control features, blueBriX ensures secure, role-specific, and attribute-driven access to healthcare data, enabling providers to deliver informed and efficient care while safeguarding patient privacy.
Future of Access Control in Healthcare
Access control in healthcare is undergoing transformative changes, with new technologies improving security and operational efficiency. Here’s an in-depth look at future trends, their impacts, and examples of successful implementations:
Emerging Trends in Access Control Technology
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can analyze access patterns, detect anomalies, and provide proactive security measures to identify potential threats. AI-driven systems adapt to usage patterns, helping healthcare facilities dynamically adjust access privileges and identify unusual access events swiftly.
Facial Recognition and Biometrics: Biometric technology, including facial and fingerprint recognition, offers precise identification and access control, especially useful in high-security areas such as pharmacy storage and patient data centers. Facial recognition is also contactless, reducing physical interactions, which is advantageous for infection control.
Cloud-Based Access Solutions: Cloud technologies enable real-time updates, access logs, and remote management of access permissions, essential for healthcare facilities with multiple locations. These systems allow healthcare administrators to adjust access settings immediately in emergencies or during high-risk situations.
Potential Impacts on Patient Care and Hospital Efficiency
Enhanced Patient Privacy and Data Protection: Advanced access control minimizes unauthorized access to sensitive patient information, complying with regulations like HIPAA, which is crucial as healthcare digitization grows.
Improved Operational Efficiency: AI-driven access control reduces manual tasks, as staff access is automatically monitored and controlled. This automation allows healthcare professionals to spend more time on patient care rather than administrative tasks, thereby enhancing overall hospital efficiency.
Crisis Response and Infection Control: Contactless access technologies and remote control of access points are particularly valuable in emergency scenarios, like outbreaks, as they allow seamless lockdowns and prevent potential virus spread by minimizing surface contacts.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations in Healthcare
Facial Recognition for Infection Control: During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals implemented facial recognition to grant entry to authorized personnel without contact, enhancing infection control and securing facilities against unauthorized access. This approach has since been used in high-risk zones and is proving effective in ongoing healthcare settings.
AI in Access Auditing: Healthcare facilities like large university hospitals have incorporated AI-driven access audits, ensuring only authorized personnel can access controlled substances and confidential patient data. These AI-based systems continuously analyze access logs to identify and respond to security threats proactively.
These emerging access control technologies are poised to create safer, more efficient healthcare environments, helping facilities manage security, streamline operations, and better protect patient information and staff.
Strengthening Healthcare Security Through Access Control
Access control plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive patient data and ensuring safety across healthcare facilities. By restricting access to authorized personnel only, healthcare organizations can prevent unauthorized access to medical records, secure areas, and other critical infrastructure. Access control measures help maintain compliance with data privacy regulations like HIPAA and can reduce risks associated with data breaches and theft.
Given the rise in cyber threats and the sensitive nature of healthcare data, prioritizing robust security measures is imperative. Healthcare organizations should implement advanced access control systems, such as multi-factor authentication, secure by design protocols, and regular audits, to bolster facility security and data integrity. This proactive approach not only protects patient information but also ensures the safety and efficiency of healthcare operations.
Worried about your facility’s data privacy? Let’s connect to discuss how blueBriX access control can resolve it!